At iupac standard temperature and pressure 0 c and 100 kpa dry air has a density of 1 2754 kg m. Air is mostly made of oxygen and nitrogen.

At 20 c and 101 325 kpa dry air has a density of 1 2041 kg m.
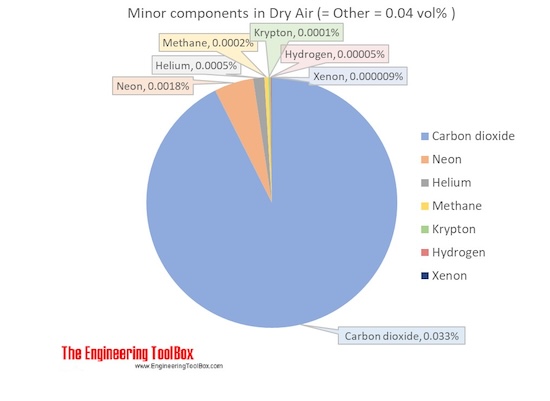
Molecular weight of air. Air is a mixture of several gases where the two most dominant components in dry air are 21 vol oxygen and 78 vol nitrogen. Oxygen has a molar mass of 15 9994 g mol and nitrogen has a molar mass of 14 0067 g mol. The molecular weight of air is approximately 28 97 g mol.
The molecular mass is estimated using the weights of all of the elements contained in air. Air is mostly made of oxygen and nitrogen. Air is a mixture of several gases where the two most dominant components in dry air are 21 vol oxygen and 78 vol nitrogen.
Oxygen has a molar mass of 15 9994 g mol and nitrogen has a molar mass of 14 0067 g mol. Since both of these elements are diatomic in air o2 and n2 the molar mass of oxygen gas is 32 g mol and the molar mass of nitrogen. Dry air has a molar mass of 0 029 kg.
Pollution in the air is not only a threat to the environment but to human lives. Compute answers using wolfram s breakthrough technology knowledgebase relied on by millions of students professionals. Using 1 25 atm of propane in a 150 ml.
In order to maintain the outlet pressure the feed flow rate has to. Molecular weight of common gases including air steam natural gas. Molecular weights of common gases including molecular mass of air ammonia natural gas water vapor.
Follow us on twitter question remark. Contact us at contact. This quantity may vary slightly depending on the molecular composition of air at a particular location.
At iupac standard temperature and pressure 0 c and 100 kpa dry air has a density of 1 2754 kg m. At 20 c and 101 325 kpa dry air has a density of 1 2041 kg m. At 70 f and 14 696 psi dry air has a density of 0 074887 lb ft.
If average molecular weight of air 29 then assuming n 2 and o 2 gasses are there which options are correct regarding composition of air. 1 75 by mass of n 2 2 75 by moles n 2. As an example the average molar mass of dry air is 28 97 g mol.
Molar mass is closely related to the relative molar mass m r of a compound to the older term formula weight f w and to the standard atomic masses of its constituent elements. Molecular mass or molar mass are used in stoichiometry calculations in chemistry. In related terms another unit of mass often used is dalton da or unified atomic mass unit u when describing atomic masses and molecular masses.
It is defined to be 1 12 of the mass of one atom of carbon 12 and in older works is also abbreviated as amu.